So, what is the difference between PON, POL, G-PON and OLAN? Do these alphabet soup acronyms all relate to the same thing and can they be used interchangeably? The answer is no – they are not exactly the same and they do have important differences.
Passive Optical Network (PON) is an umbrella industry term for fiber-based access networking architecture that is used in both 1) enterprise passive optical local area network inside buildings and across campus and 2) residential fiber-to-the-premises network that can connect a home, apartment and a business across a city.
- Passive Optical LAN (POL)
- Used inside local area networks (LAN) of buildings and across campus.
- Deployed by government, business enterprise, hospitality, education, retail, public venue and healthcare type network owners, operators and developers.
- Connects computers, phones, servers, Wi-Fi, building automation, building monitoring, building intelligence, security surveillance, all forms of enterprise video and all IP/Ethernet devices within the digital ceiling and Internet of Things realm.
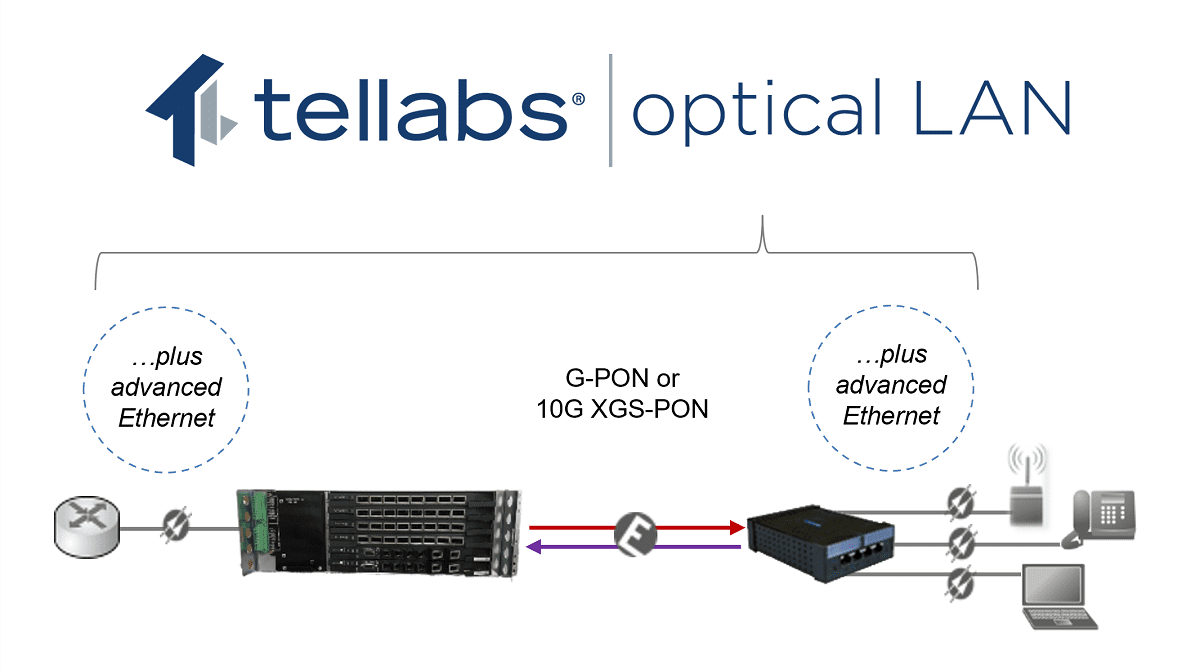
- Today, it uses Gigabit Passive Optical Network (G-PON) technology standard ITU-T 984 that provides asymmetrical 2.4Gbps downstream and 1.2Gbps upstream capacity. POL is evolving to the next generation standard called XGS-PON which is based on ITU-T 989 and will provide cost-effective symmetrical 10Gbps downstream and 10Gbps upstream capacity.
- Now, this next detail is very important because it represents the key unique difference! POL electronics manufactures make tremendous investments in additional R&D to support advance Ethernet IEEE features to satisfy true enterprise requirements (e.g. bridging, LAG, VLAN, ACL, PoE, LLDP, NAC, 802.1x, AS-SIP, PON protection, Change of Authorization, DAI, MAB, etc…). A true Passive Optical LAN will have these features.
- The Association for Passive Optical LAN (APOLAN) is the trade organization representing this segment.
- There are different branded solutions of POL by the electronics manufacturers. For example, Tellabs Optical LAN (OLAN) is the Tellabs’ branded solution.
- Fiber-to-the-Premises (FTTP) or Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH)
- Used for last-mile access network to homes, apartments and businesses across a city.
- Deployed by telecommunications service provider network operators (e.g. Verizon FiOS).
- Connects services such as high-speed internet, phones, TV and residential Wi-Fi.
- It too currently uses Gigabit Passive Optical Network (G-PON) technology standard ITU-T 984. However, FTTP is evolving to the next generation standard called NG-PON2 which is based on ITU-T 989 and is a more costly and complex 40Gbps solution.
- Fiber Broadband (formerly FTTH Council) is the industry organization representing this segment.